Introduction
- In this tutorial, you will learn how to add an admin table which is similar to admin posts or pages or comments table list
- Our table list is a merged list of all searchable post types post which are in draft mode i.e. not yet published or still work in progress posts
- Based on this tutorial you will learn how to implement the following features
- Search box
- Filter dropdown (Post type)
- Bulk action (Trash multiple posts at a time)
- Action quick links (Each post have edit, trash & view)
- Pagination
- Our custom table is a child class of the official table class: WP_List_Table
- We will explore each and every method in its individual section
- GitHub link to directly activate as a plugin while learn/play with the source
Complete Source Code
Include Base Class
- In the complete source code gist (from now onwards we call it as main gist/file), you can find that we included our base class at line no: 24 though most of the time the class
Drafts_List_Tabledirectly extend the classWP_List_Tablewithout the include once but WordPress functioning based on hooking process so sometimes our class may be called before hooked and globally included theWP_List_Tabletherefore it’s always better to check if it’s included or not and included the class file - Also instead of hopping here and there, we can add the snippet which is related to the current context so we include partial code gist like this
Extend Base Class
- We extend our table class
Drafts_List_Tablefrom core WordPress classWP_List_Tableat line no: 35 like this
Class Constant & Property
- The class
Drafts_List_Tablehave one constantPOSTS_PER_PAGEand one private property$allowed_post_types(main source code line no: 40) - The
POSTS_PER_PAGEis to stores an integer value which is the number of maximum posts to be shown in the table per page - The property
$allowed_post_typeshave an array of post types that can be queried and used to list out all posts that come under these post types
Constructor
- Our constructor (main source code line no: 52) is not that much fancy it has two simple statement one is a parent constructor call with three arguments
singular,pluralboth for labeling purpose andajaxaccepts boolean to decide whether HTTP calls are ajax based or not - The other one calls the class method
allowed_post_types()and stores the return value in the private propertyallowed_post_types
Get Allowed Post Types
- This method is placed inside this class is for tutorial purpose only (but for the real-life project, my suggestion is to create a utility or helper module which may have more helper classes like one for UI works, another API services, and other for wrapping commonly used DB queries likewise we can build n-number of classes for different common purposes)
- Let’s place the architectural suggestions aside and focus on this tutorial, the method
allowed_post_types( main source code line no: 71 ) will return the post types in the array - Line no 9: by using WP core function
get_post_typeswe fetch the post types in our web application here we pass an argumentpublicwith the boolean valuetruetherefore it returns only publicly accessible post types - Visit documentation for more details about the function
get_post_types - We unset the attachment post type to exclude that kind of posts from the table list and finally returned the remaining post type as an array
Convert Slug String To Human Readable
- Yes, this method (main source code line no: 85) also another good candidate for the utility method
- This method converts the slug to readable format i.e. it replaces all underscore symbol with white space and title cased the words
Convert Post Types Human Readable
- The method
allowed_post_types_readable(main source code line no: 94) is iterate on all allowed post type and convert the post type’s slug into human-readable - The inner working of this method is using the PHP function
array_mapwe pass ourhuman_readableas a callback that applies on each value of the private array propertyallowed_post_types - The newly generated array is assigned to the variable
$formattedand the same is returned
Create Custom WP_Query Object
- This method
get_posts_object(main source code line no: 108) is the data fetching method of this custom admin table class
- As this method is a little lengthier let’s try to refer to each statement using its gist line number for easier understanding, here all the line numbers pointing to the gist
get_posts_object.php - Line no 9: fetching private array property
allowed_post_typesthen assign it to the method’s local variable$post_types - Line no 11: we declare a local variable
$post_argswhich holds initial argument we pass to theWP_Queryinstance constructor call - The
$post_argsis an associative array with the following key-value pair- The key
post_typeholds the array of post types - The key
post_statusholds the array of statuses to fetch here we pass only one value i.e.draft - The key
posts_per_pageholds the integer value which controls how many posts to show on the page
- The key
- Line no 17: the local variable
$pagedis fetch page number from query string by using the PHP functionfilter_inputto validate if it’s an integer or not using the filter idFILTER_VALIDATE_INT - Line no 19: if the variable
$pagedhaving truth value then assign the value stored in$pagedto$post_argsarray keypaged - Line no 23: the local variable
$post_typeis fetching post type (which we can use to filter the table to show only specific post type posts only) from query string by using the PHP functionfilter_input, sanitized the incoming string using the idFILTER_SANITIZE_STRING - Line no 25: if the variable
$post_typehaving truth value then assign the value stored in$post_typeto$post_argsarray keypost_type - Line no 29: the variable
$orderbyaccepts the table column name, as the value get from the query string it’s good to sanitize it - WordPress provided a sanitize function sanitize_sql_orderby which is specifically deal with the order by clause with or without sort order
- Using the
sanitize_sql_orderbyfunction we sanitized the column name - Line no 30: the filtered query string order’s value is passed to WordPress function esc_sql for escaping if any SQL injection character present
- Don’t accept user’s data blankly always do escaping, sanitization, and validation (skip sub-points if you need)
- Four years back got a chance to audit a project, the theme is adding a music file name and it’s CDN path to DB in the insert query without escaping or doing some other alternative like a prepared statement or PDO the source code inserts the file name
- When sending back the review to the concerned team they asked “why we need to escape? it’s just a filename of an MP3 file”
- I replied that we need to escape the filename because various bands have an apostrophe in their band name like
Guns N' Rosestherefore please escape the user input - Thank god the application is Indian based music and running happily without unintentional SQL injection by the web application user because most of the Indian name or band name doesn’t have an apostrophe
- But the piece of advice is, in order to break your web application no need to hire a hacker just make it famous, and more user using it you will get to know why I’m insisting this
- Line no 32: if the variable
$orderbyis empty then set a default valuedate, then our posts are sorted by the date column - Line no 36: if the variable
$orderis empty then set a default valuedesc, then our posts are sorted in descending order i.e. reverse chronological order - Line no 40: assigning the order by value into the variable
$post_argsassociative indexorderbywhich we pass an argument to theWP_Queryclass first parameter - Line no 41: this statement also similar to the previous one at line no 40
- Line no 43: in the variable
$searchfetching the query stringsand passed it to theesc_sqlfunction, this query stringsonly available when the user did a search - Line no 44: as said in the previous point the
savailable only on search therefore before assigning we doing a conditional check to verify it’s not empty - Line no 45: once the not empty condition passed we assign the search value into the associative index
sof the variable$post_args - Line no 48: finally we pass the
$post_orgsto the classWP_Queryand return the query class object
No Items Text Display
- The method
no_itemsis overridden method of the base classWP_List_Table - The purpose of this method is to display the information when no posts are available
- Line no 7: displaying the message about no posts which properly escaped for HTML and can be translated by using the WordPress function
esc_html_e
Display Default Column
- Line no 10: the overridden method
column_defaultis used to handle the column output - Internally this method is called for each column this method accepts two parameters
$itemhave all the current row’s columns values in associative key-value pair$column_namecurrent column name
- Line no 11: declared and initialized the variable
$resultwith empty string which we use to assign the column data to be shown - Line no 12: switch statement will switch and create the column value based on the passed column name
- Line no 13: the
datecase is used to display date in two variant either by date if the post created date is more than one day else returns how human saying the date for e.g.10 minutes ago - Line no 14: using the WordPress template function
get_the_timeretrieve the post created time with formatting, get_the_time to learn more - Line no 15: the function
get_post_timestampis used to retrieve the draft post published time in unix timestamp format, get_post_timestamp to learn more - Line no 16: took the seconds difference of current unix timestamp (using PHP function time) and post created time and assign it to the variable
$time_diff - Line no 18: we’re checking the time is less than a day if so then display the time in human readable format using the WordPress formatting function human_time_diff
- Line no 22: else will show the date in the format
Y/m/d - The remaining cases (
authorandtype) are self explanatory
- Line no 13: the
- Line no 37: return the variable
$resultwhich have the value to show in the specific column
Display Table Header
- The method
get_columns( main source code line no: 200 ) is an inherited must overridden method which is responsible for displaying the table headers - For a quick view please see the snippet of the main source below
- This method simply returns the array of key-value pair of columns which have a set of an internal name as key and it’s display value as the value
Title Column Callback
- The method
column_title(main source code Line no: 216) is used to display the HTML in the table columnTitle - Internally this method is called by the parent method
single_row_columnselseif is called thecolumn_titlemethod dynamically using the callback logic
- Line no 10: using the WordPress function get_edit_post_link we fetch the edit link for the current post in the table row looping flow
- Line no 11: get_permalink is used to fetch the current post permalink
- Line no 12: get_delete_post_link is used to fetch the delete link of the current post
- Line no 14 – 36: is simple HTML generation to display in the
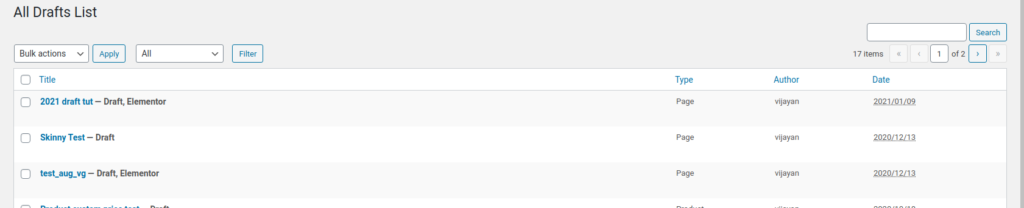
Titlecolumn by returning the variable$output, in these statements, the only thing we need to focus on is a template function _post_states - The function
_post_statesis used to display post states as HTML for e.g. in the Introduction section if you see the sample image there are two things displayed in post statesDraft, Elementor - The state
Draftis fetched by core WordPress whereasElementorfetched by Elementor plugin to notate this post is formed by Elementor page builder
Column Checkbox
- The method
column_cb(main source code line no: 251) is a simple method to display a checkbox in each row to select the post for bulk action like trashing an unneeded post
Build Table Data
- The method
prepare_items(main source code line no: 264) is the core part to create the data for the table note here I’m saying about an array of information to show on the table, not the HTML design part
- Line no 9: called the method
get_columnsto fetch an array of column names to be shown in the header of the table - Line no 10: called the method
get_sortable_columnsto fetch an array of sortable data in the format of an internal name as key and sorting option as a value such asarray( column_internal_name, sorting_type)and assign it to the variable$sortable(don’t worry we will see more detail when we explain this method we will see the detailed way) - Line no 13: the parent class property
_column_headersaccepts an array of arrays as in this order first array of columns to be shown in the table, second an array of columns which are hidden one, third array of sortable columns, fourth a string denote which column is primary one - Line no 16: called the method
process_bulk_actionwhich is responsible for bulk actions like trashing the posts - Line no 18: called the method
get_posts_objectwhich return theWP_Queryinstance with whatever filters and sorting options are applied, that instance is assigned to the variable$get_posts_obj - Line no 20: check if the queried
WP_Queryinstance have posts object using the method$get_posts_obj->have_posts() - Line no 22: if posts are available then begin the looping
while ( $get_posts_obj->have_posts() ) - Line no 24: the
WP_Querymethodthe_postis used to retrieve the next post internally which setsWP_Querypropertyin_the_looptotrueand retrieves the next post - Line no 26: form the array of data therefore each index have an array of values to show in each row of the table, the formation of this array mostly using WordPress template functions
- Line no 34: the function
wp_reset_postdatais used to reset the global variable$postto the main query’s current post after completing our custom query loop - Line no 37: Assign our looped collection of table data to the parent class
WP_List_Tablepropertyitemstherefore other methods that require data can access from this property - Line no 39: the parent class method
set_pagination_argsis responsible to set pagination related information to the parent class property_pagination_argshere we basically set up our pagination using three itemstotal_itemswe pass theWP_Querypropertyfound_postsper_pagewe pass theWP_Querypropertypost_counttotal_pageswe pass theWP_Querypropertymax_num_pages
Create Bulk Action Dropdown
- This method (main source code line no: 309) return array of key-value pairs which is used to show in the bulk action dropdown (if you like to know how the HTML formed by retrieving the return value of this method then please check bulk_actions method of the parent class
WP_List_Table)
Process Bulk Actions
- This method
process_bulk_action(main source code line no: 320) is used to do bulk actions like trashing the post likewise you can change the state of many posts (for e.g. change the set of posts from draft to publish) or process many posts data altogether (for e.g. trigger email to multi-selected users and change the custom state pending to invited)
- Line no 9: in the conditional statement, we check whether the current action is trash if so then execute the inner block
- Line no 10: the variable
$post_idshold get query valuedraft_idwhich is a collection of ids of the posts that need to be trashed - Line no 12: verify is the variable
$post_idsis an array - Line no 13: convert all elements in the array into an integer value the reason is we received it from the get query therefore it will be a string and sometimes may have illegitimate data if the user intentionally add some junk data, here we iterated over each element using
array_map - Line no 15: we check this in
ifcondition to confirm at least one element present in the$post_idsarray - Line no 16: pass all the ids to the WordPress function wp_trash_post which will trash the posts
Display Actions, Filters, and Pagination
- The method
display_tablenav(main source code LINE NO: 341) is an overridden method that is responsible for displaying bulk actions, filters dropdown, and pagination which accepts a single argument with a value of eithertoporbottombased on that display the block of HTML at the top or bottom of the table
- Line no 12: created the navigation wrapper div with a dynamic class
toporbottombased on the argument$whichvalue - Line no 14: verify is the table has items to display
- Line no 16: if has items then display the bulk action dropdown
- Line no 20: the method
extra_tablenavis used to display additional filter we will see more detail about this method in the next section - Line no 21: the method
paginationis the parent class method that handles the pagination of the table
Extra Table Navigation HTML
- The method
extra_tablenav(main source code line no: 367) is used to display additional filter controls here using the argument$whichwe controlled our filter to display only at the top of the table
- Line no 12: conditionally show our filter only at the top by checking the
$whichargument value is equal totop - Line no 13: create a multidimensional associative array
$drafts_dropdown_argwhich we pass to the methodhtml_dropdownwe will see more about this method in the next section - In the variable
$drafts_dropdown_argtheoptionsindex has the value to show in the dropdown - The
containerindex has the class name to add to the dropdown component’s container div - The next two indexes
labelandselectrepresents its tag name, and it holds attributes of that tag in the inner array as key-value pair - Line no 31: using the WordPress function submit_button echoes our submit button
UI Helper HTML Dropdown
- The method
html_dropdown(main source code line no: 399) is used to generate HTML dropdown dynamically which is wrapped inside container div also to be clear this method needs to be added to the utility classHelpertherefore the same method can be used in many other places too but for this tutorial, I added this inside the same class
- This method is simple string interpolation of passed argument into the custom HTML it’s pretty easy to understand, and I believe there is no need for a very detailed explanation
Sortable Column
- The method
get_sortable_columns(main source code line no: 434) is an overridden method that simply returns an associative array
- Line no 11: the key is the column internal name and the value is an array that represents the behavior of the sorting
- Here we followed the format
'internal-name' => array( 'column', 'is_descending') - The boolean
falseis no need to pass explicitly (see implementation logic) but for clarity here I passed instead of that if you alter it totruemeans on initial page load that column will be sorted in descending order
Column CSS
- This anonymous function (main source code line no: 448) inject custom HTML in the header part because we used the
admin_headtag (this snippet only load in the admin part, not for the user-facing frontend pages if you would like to load on frontend then use the tagwp_head)
- Line no 9: fetch the current page name from the global get query string
- Line no 10: check the page name is not equal to
all-draftsthen bypass the upcoming execution by executing the voidreturnstatement - Line no 15: add CSS
widthproperty to the columntypei.e. post type column therefore which will give more space or real-estate to the columnTitle
Admin Menu For Drafts Table
- Using the hook
admin_menu(main source code line no: 465) we hooked our drafts table admin page
- add_menu_page for more details about each argument and its purpose
Instantiate Draft Table
- The function
bootload_drafts_table(main source code line no: 483) is a callback function attached to theadd_menu_page, we pass this as a second from the last argument
- Line no 7: instantiate custom admin table class
Drafts_List_Table - Line no 12: pass draft table page menu slug
all-draftsas hidden value therefore whenever the user does a submit action like searching, after every new request the filtered table is shown at the right page - Line no 15: the method
prepare_itemsis the workhorse of this class which handles all table data generation and processing logic - Line no 16:
search_boxis the overridden method that accepts two parameters are a label of the submit button and an HTML id attribute for the search input field here we pass the first argument i.e. label asSearchand the second argument i.e. id assearch - Line no 17:
displayis a parent class method that is responsible for displaying or echoing the HTML table with dynamic data, actions, filters, and pagination
Conclusion
- Through this tutorial, you learned how we can create a custom admin table on WordPress
- Simultaneously using this knowledge you understand how WordPress posts, pages, and comments table are formed
- Not only WordPress core many plugins like WooCommerce, SEO by Rank Math, and many other plugins more or less follow the same procedure therefore it’s easy for you to understand their admin table source
- By learning this tutorial now you’re comfortable with WordPress core class
WP_List_Table